Body - Fields¶
Just like Path and Query, you can use Pydantic's Field in Body to declare validation rules within a model and provide additional metadata. This allows you to define validation for request bodies more clearly in your API.
import Field¶
First, you have to import it:
from typing import Annotated
from nexify import Body, Nexify
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
app = Nexify()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Annotated[
str | None,
Field(
default=None,
description="The description of the item",
max_length=300,
),
]
price: Annotated[
float,
Field(
gt=0,
description="The price must be greater than zero",
),
]
tax: Annotated[
float | None,
Field(
default=None,
gt=0,
),
]
@app.post("/items")
def create_item(item: Annotated[Item, Body()]):
return item.model_dump()
Declaring Model Attributes¶
You can then use Field with model attributes:
from typing import Annotated
from nexify import Body, Nexify
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
app = Nexify()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Annotated[
str | None,
Field(
default=None,
description="The description of the item",
max_length=300,
),
]
price: Annotated[
float,
Field(
gt=0,
description="The price must be greater than zero",
),
]
tax: Annotated[
float | None,
Field(
default=None,
gt=0,
),
]
@app.post("/items")
def create_item(item: Annotated[Item, Body()]):
return item.model_dump()
You can use the same properties as in Path and Query, including:
gt,ge,lt,le: Constraints for numeric values (gt=0 means greater than 0, ge=0 means greater than or equal to 0)min_length,max_length: Constraints for string length (min_length=2, max_length=50)regex: String validation using regular expressions (regex="^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+$")
In addition to these, various other options are available. For more details, refer to the Pydantic official documentation.
Adding Extra Information Using Body()¶
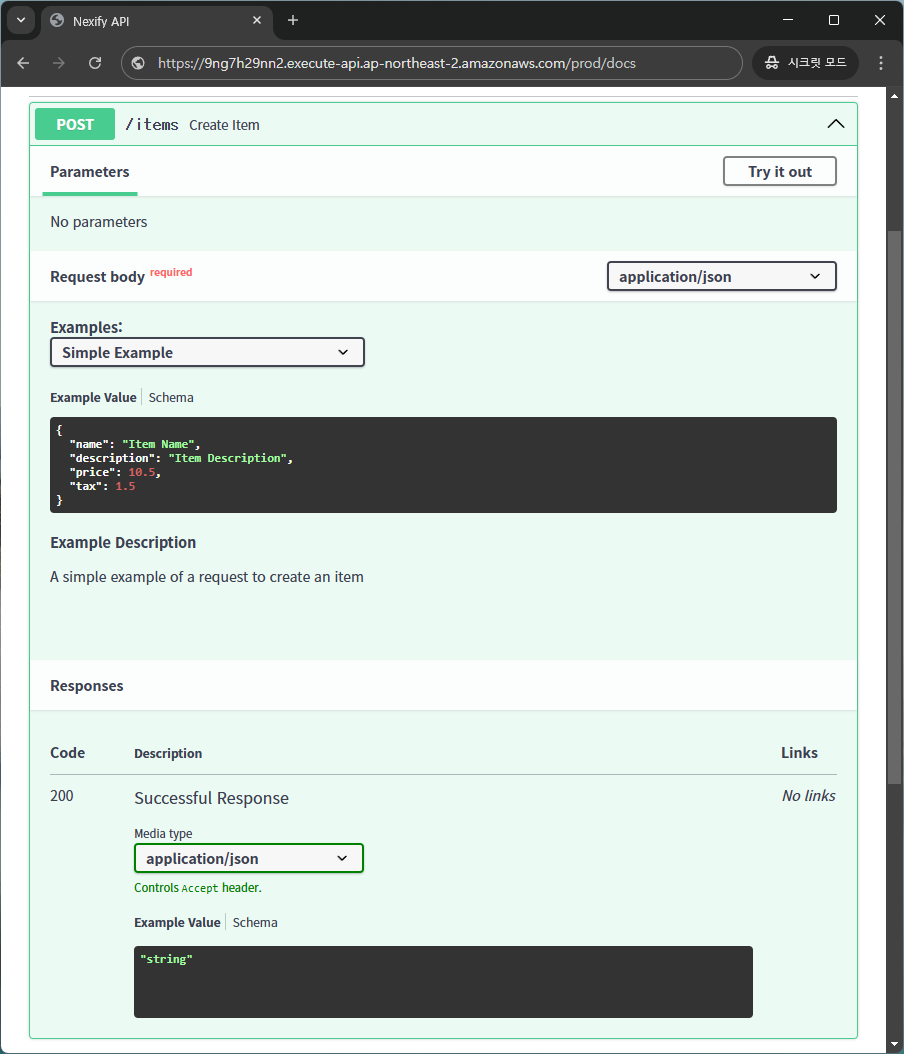
You can use openapi_examples inside Body() to define example values that will be displayed in the API documentation.
from typing import Annotated
from nexify import Body, Nexify
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = Nexify()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
@app.post("/items")
def create_item(
item: Annotated[
Item,
Body(
openapi_examples={
"simple_example": {
"summary": "Simple Example",
"description": "A simple example of a request to create an item",
"value": {
"name": "Item Name",
"description": "Item Description",
"price": 10.5,
"tax": 1.5,
},
}
},
),
],
):
return item.model_dump()
In this case, you can see the example values in the API documentation.
Info
You can also set a example value using Field(..., example=1234), but if you want to add more detailed examples to your OpenAPI documentation, it is recommended to use openapi_examples inside Body().